A couple of articles that look at cholesterol levels and PD.
The results suggested that elevated serum levels of triglycerides (TG), low density cholesterol (LDL) and total cholesterol (TC) may be protective factors for the pathogenesis of PD.
And here’s another meta analysis that bottom lines the results in the title:
This meta review looked at
- total cholesterol (TC),
- triglycerides (TG),
- high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C), and
- low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C).
Fifteen cohort studies with 9740 participants, including 2032 PD patients and 7708 controls were analyzed, and the analysis found that lipid levels in the PD patients was significantly lower than that of healthy controls. So dyslipidemia might have a predictive value.
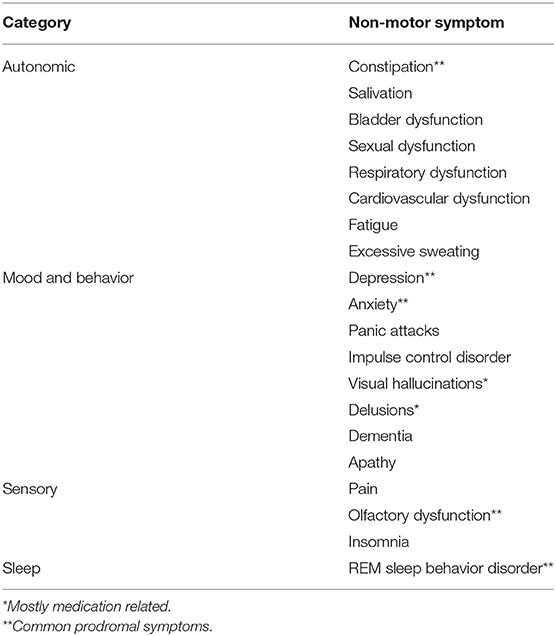
As a Person With PD (PwP), this sort of information could have been useful, say, oh, between 50 or 60 years ago. Of course, it would have taken general practitioners with a broad knowledge of factors affecting the prodromal symptoms and signs of PD to pick up on it. (And that information wasn’t available at that time).
As it so happened, I had essential tremors, and could feel resting tremors oscillating away, even though they were not visible to the human eye. And other prodromal symptoms were present, too, and at an early age. Fortunately, I did not have the LRRK or PARK gene variations that cause early onset PD that can not be denied (Michael J. Fox’s case comes to mind). Unfortunately, my particular set of symptoms did not result in an actual diagnosis of PD until after I had been retired early due to one of my other prodromal symptoms (MDD) put me on disability leave for over 9 months, and I was unable to hold down a steady job for a couple of years. Fortunately, the Social Security Administration provided me with retroactive disability benefits to the day following the date the insurance company gave up on trying to recoup their losses by representing my case to the OASDI. Fortunately, I have been able to find folks who have supported me through the years, intellectually and socially, as my continuing journey with PD has become a larger part of my life.
Perhaps the future of medicine lies in something like the application of IBM’s Big Blue computer (or other advanced Artificial Intelligence systems) to assimilating the huge (not just big) data residing in the NIH and other medical libraries, so that correlations among various signs could be identified and point to diagnostic criteria and effective treatment modalities, so that until there is a cure for Parkinson’s (and other diseases), we can do what we can to identify the probability of an eventual diagnosis (provided decent medical information and observations) and then to defer or delay and to mitigate the symptoms.
And until then, I will do my best to forgive those who have caused me harm, whether through omission or commission, while asking forgiveness of those against whom I have “trespassed,” to use the word in the KJV.
(Didn’t mean to take an ethical/religious tangent at the end, but there it is. I’ve said too much, I haven’t said enough… I was sentenced to twenty years of boredom, for trying to change the system from within…[insert your favorite poplar song phrase here]).
###